What is Emerade used for?
Emerade™ (sterile epinephrine solution for injection in a pre-filled pen) is now available for the emergency treatment of anaphylactic reactions in patients who are determined to be at increased risk for anaphylaxis, including individuals with a history of anaphylactic reactions. Emerade is intended for immediate self-administration for emergency treatment of severe allergic reactions , including anaphylaxis associated with peanuts, tree nuts, shellfish, fish, milk, eggs, and wheat, stinging insects and medications
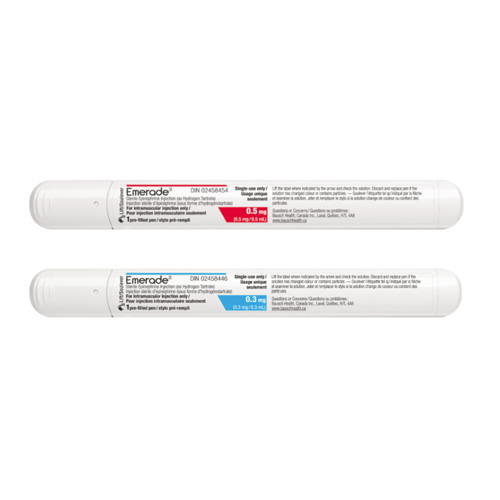
Emerade is intended for the treatment of serious allergic effects and allows time to seek emergency treatment. Emerade is currently available in a 0.3 mg dose for children over 30 kg bodyweight, adolescents and adults who weigh 30 to 60 kg (66 to 132 lbs) and a 0.3 mg or a 0.5 mg dose for adolescents and adults weighing 60 kg (132 lbs) or more, depending on clinical judgment. This can have other adverse reactions that are unpleasant. Emerade contains epinephrine which helps recover from these effects. Inform your doctor if you have a history of serious allergic reactions or anaphylaxis so they can look into your treatment options. There can be risks and for people with severe allergies need appropriate solutions.
Emerade Information
How to Use Emerade?
EMERADE should be used for intramuscular injection only on the outer thigh. The injection occurs when the triggering cylinder is gently pressed into the thigh. This can be done through clothing due to the 25 mm needle length.
Press EMERADE gently against the outer side of the thigh. A click can be heard when the injection goes into the muscle. Hold EMERADE against the thigh for about 5 seconds. Lightly massage the injection site afterwards.
Once you have used the injection seek immediate medical attention. If there is no improvement or your condition worsens within 10 minutes, use another if you have one available. If you accidentally inject the device incorrectly you may need to have another device as a back-up.
Emerade Drug Interactions
- bromocriptine
- cocaine
- hyaluronidase
- dipivefrin
- medications used to treat an abnormal heart rhythm (e.g., amiodarone, sotalol, quinidine, procainamide)
- certain antihistamines (e.g., diphenhydramine, tripelennamine, chlorpheniramine)
- cannabis
- nabilone
- diabetes medications (e.g., chlorpropamide, glipizide, glyburide, insulin, metformin, nateglinide, rosiglitazone)
- methylphenidate
- caffeine
- amphetamines (e.g., dextroamphetamine, lisdexamfetamine)
- monoamine oxidase inhibitors (MAOIs; e.g., moclobemide, phenelzine, rasagiline, selegiline, tranylcypromine)
- atomoxetine
- phenothiazines (e.g., chlorpromazine, perphenazine, prochlorperazine)
- serotonin/norepinephrine reuptake inhibitors (SNRIs; e.g., desvenlafaxine, duloxetine, venlafaxine)
- beta-blockers (e.g., propranolol, atenolol, metoprolol)
- decongestant cold medications (e.g., phenylephrine, pseudoephedrine)
- norepinephrine
- long-acting bronchodilators (e.g., formoterol, salmeterol)
- decongestant eye drops and nose sprays (e.g., naphazoline, oxymetazoline, xylometazoline)
- tricyclic antidepressants (e.g., amitriptyline, desipramine, nortriptyline)
- fast-acting bronchodilators (e.g., salbutamol, terbutaline)
- diuretics (water pills; e.g., hydrochlorothiazide, indapamide, furosemide)
- ergot alkaloids (e.g., ergotamine, ergonovine)
- theophyllines (e.g., aminophylline, oxtriphylline, theophylline)
- linezolid
- digoxin
- alpha blockers (e.g., alfuzosin, doxazosin, tamsulosin)
- spironolactone
- levothyroxine
- cabergoline
What are Side Effects of Emerade?
- sweating
- restlessness
- weakness
- paleness
- irregular heartbeat
- vomiting
- throbbing
- anxiety
- tremors
- chest pain
- dizziness
- increased heart rate or pounding heartbeat
- nausea
- symptoms of a stroke (e.g., sudden blurred vision, difficulty speaking, dizziness, headache, weakness)
- difficulty breathing
- tenseness
- fear
- shakiness
- headache
